Introduction
This article covers basic introduction to the cryptocurrency arbitrage and its profits, together with couple of examples. It also describes in detail basic arbitrage strategy with withdrawals. The idea is to buy cheap on exchange A, transfer to the exchange B where you can sell for more and sell. At the end to go through the full circle, send what you’ve received for the transaction from exchange B to exchange A. Repeat…
Difficult beginnings
The first time when I’ve noticed that I could buy Bitcoin cheaper on Poloniex than on Binance it was a blast for me. I thought that something was broken. That the UI of either of these exchanges doesn’t manage to display the price quickly enough, or some similar story. I couldn’t believe that this is possible at all. How come? I was sure that there is just one price of the Bitcoin. Not necessarily understanding who sets it, but I was sure it is just one. It took me some time to understand that the Bitcoin is traded on many exchanges. And that each exchange has its own price that is independent from other exchanges. And that the exchanges are not in sync! From time to time you can see one exchange offering some coin for much more than others. That is the opportunity for the arbitrage!
As soon as I understood that this is possible I thought: “I will buy Bitcoin cheap on Poloniex, then I will send it to Binance and sell it for more”. After doing this billion times I could eventually buy my lambo… If only that was so easy. With each buy/sell operation we need to pay the commission. Also, when transferring funds we are paying withdrawal fee. That means that after doing a math, the difference in the prices needs to be pretty high in order for this type of arbitrage to be profitable. The withdrawal takes time. Sometimes it takes couple of hours between the moment you withdraw the funds from one exchange and the moment when you can trade with these funds on second exchange. During this time the arbitrage opportunity may already be gone… But let’s dig deeper into this and first let’s define the basic concepts.
What is cryptocurrency arbitrage
Definition of the arbitrage after Investopedia:
Arbitrage is basically buying a security in one market and simultaneously selling it in another market at a higher price, profiting from the temporary difference in prices. This is considered risk-free profit for the investor/trader.
Profit from the arbitrage
Let’s try to define what does it really mean to profit from the arbitrage trade opportunity. In order to do this I would like you to analyse following diagram:
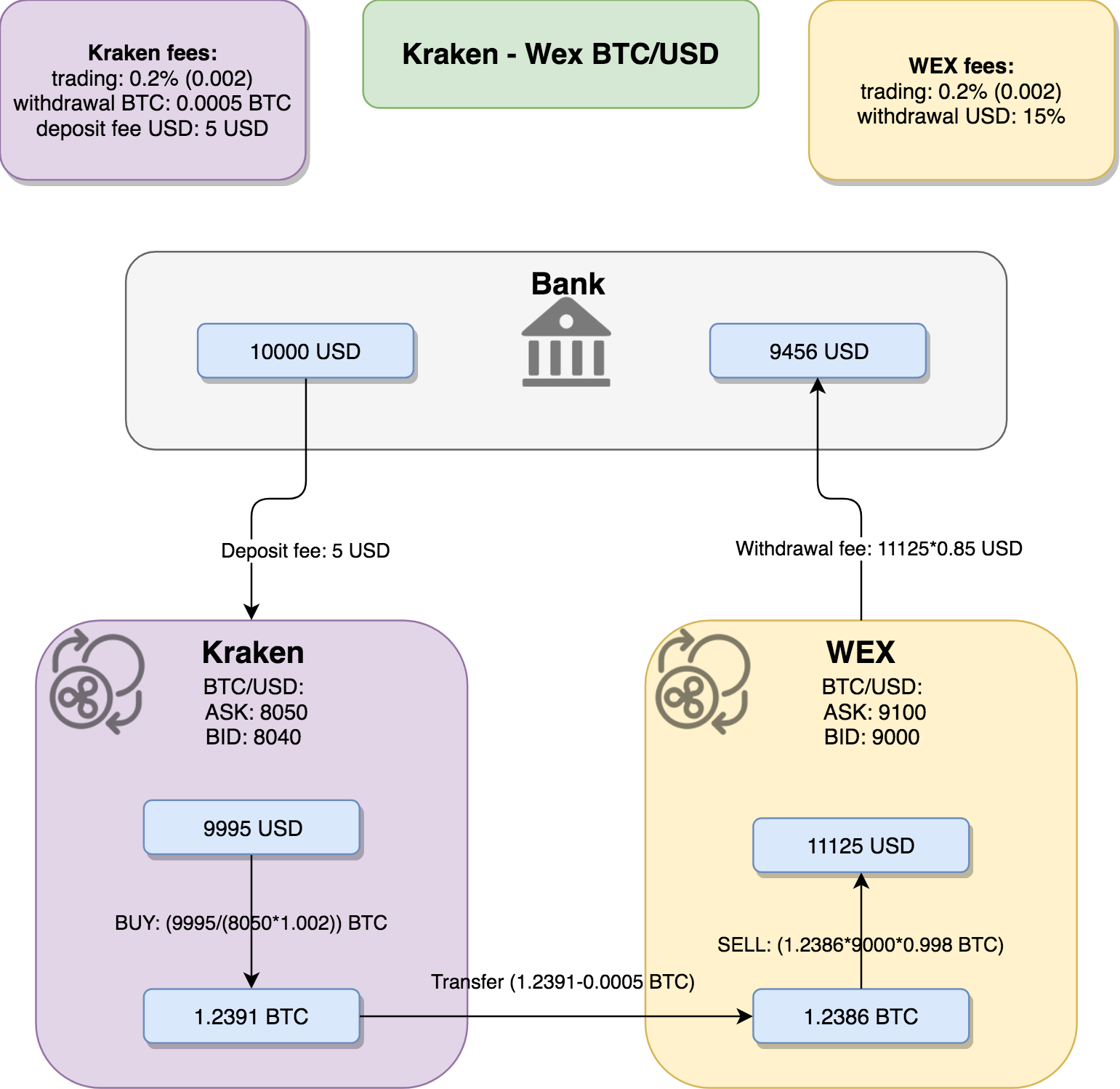
- We’ve just spotted wonderful arbitrage trade opportunity – we can buy BTC for 8050 USD on Kraken and sell it for 9000 on Wex. We are going to be rich!.
- We take our 10000 USD and we deposit them to Kraken, after paying the deposit fee we have 9995 USD.
- Then buying BTC on Kraken for all the USD we have, gives us 1.2391 BTC.
- After withdrawing this BTC from Kraken to WEX we have 1.2386 BTC as we had to pay Kraken withdrawal fee.
- And we are selling our BTC on Wex for USD. And we are rich! We have 11125 USD. 1125 USD more than when we started. This is business! We start thinking about repeating this couple of times to buy our lambo.
- But they money is still on WEX. We are checking the withdrawal fees and bang! Aw maaan… this is crazy.
- Those guys are calling 15% for the USD withdrawal. Instead of being richer, we are poorer. After withdrawing we have 9456 USD. We have just lost 544 USD.
This vivid example shows that we should not look at some intermediate steps of your arbitrage operation. In the middle of the way we may have more than we had at the beginning (in absolute numbers). We should count the profit from arbitrage trades when our base capital is back where it started, when it went through the full loop and produced some profit.
Basic “Loop” arbitrage
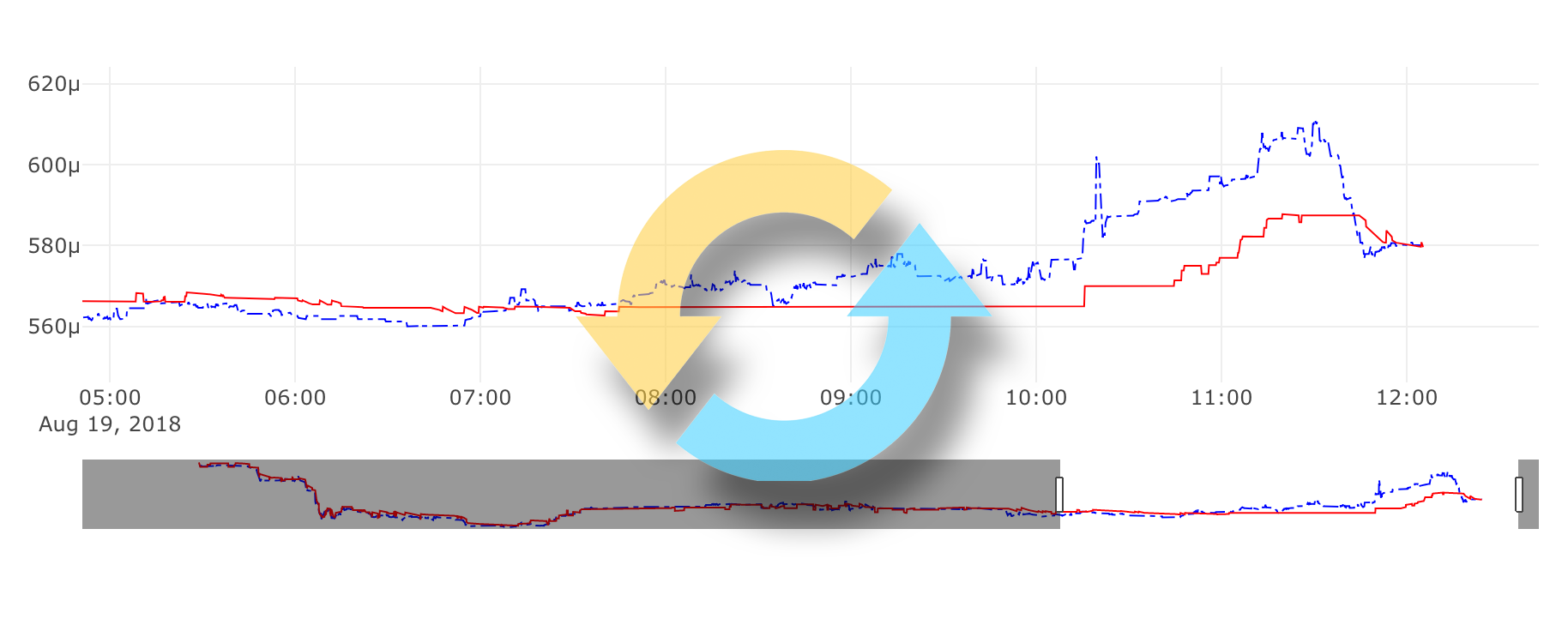
I think that the best way to understand this is go through some real case. Let’s take a look at the chart:
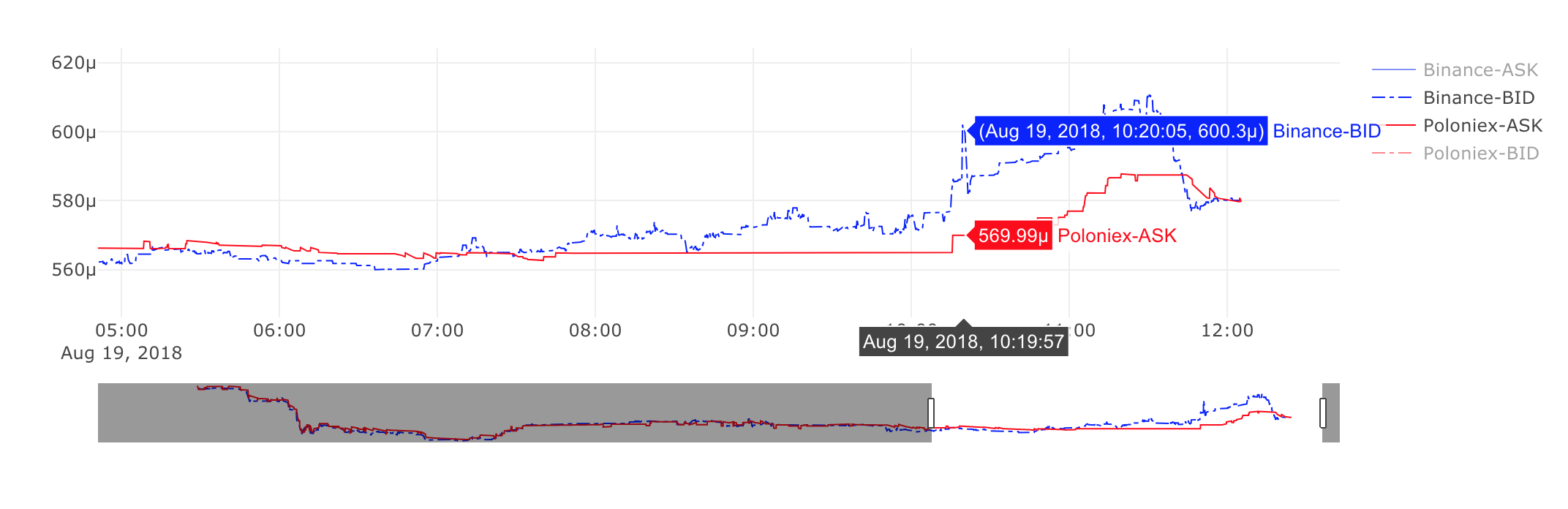
It represents the LSK price expressed in BTC (LSK/BTC pair) on two exchanges: Poloniex and Binance on 19th August 2018, from 5 am till 12pm. Red line represents the ASK price on Poloniex – that means how much we need to pay for LSK on Poloniex. Blue line is BID price on Binance – that is how much we can get for our LSK on Binance. These prices do not contain exchange’s trading fee.
Around 5 am, everything was normal, ask price on Poloniex was higher than bid price on Binance. Then starting from around 8 am, the price on Binance took off and until around 11:30 was higher than on Poloniex. In the moment of the highest difference – around 10:10, Poloniex ask price was 0.00056999 BTC while Binance bid price was 0.00060030. That is over 5% difference!
Remember that these are just ticker prices and the real price you would have to pay or you would get depends on the size of your order. Also you need to remember about trading commissions. That is where MultiTrader arbitrage analysis gets into the game – it does full cross-exchange order book matching for the size of the deal that you provide:
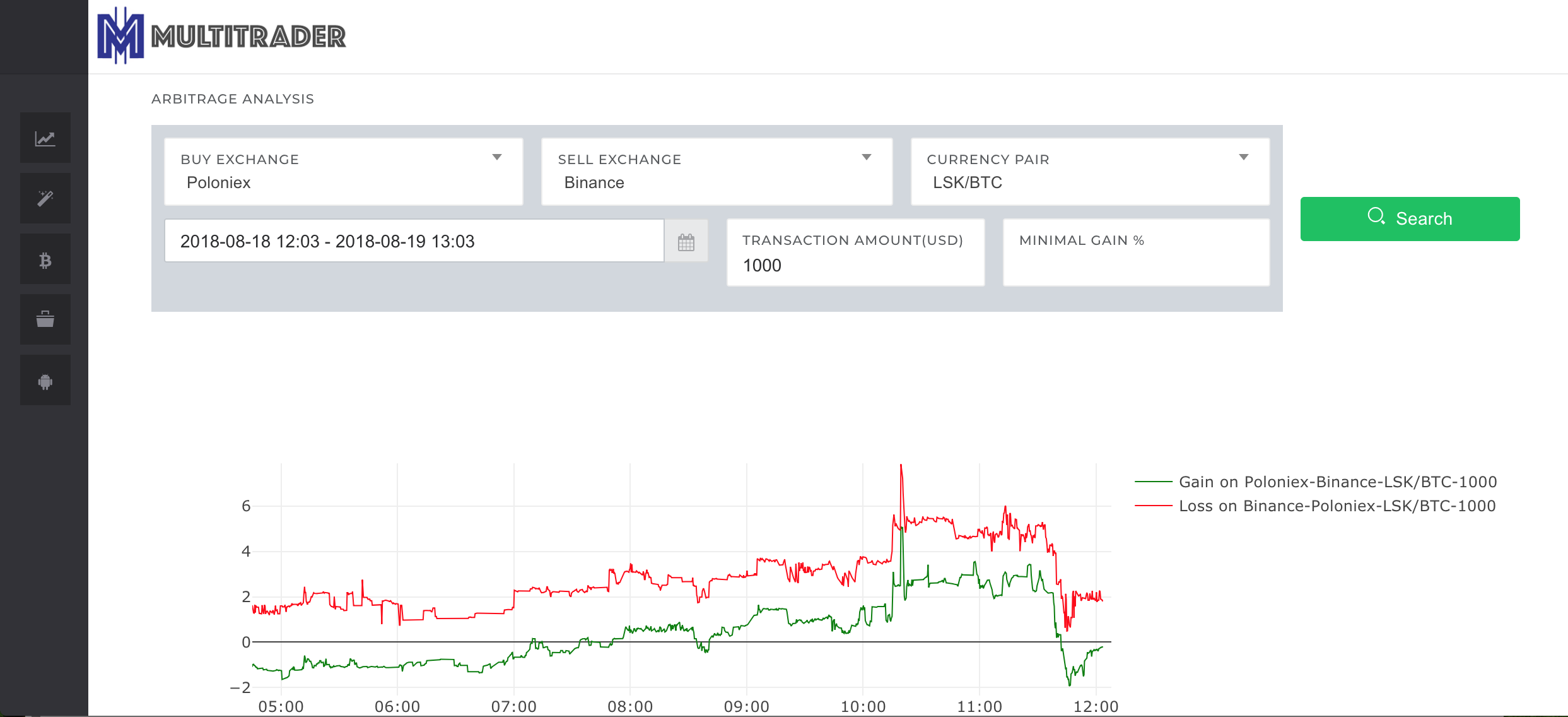
In the screenshot above you can see the arbitrage analysis for transaction size of 1000 USD. The y-axis represents percentage gain from the arbitrage. Green line represents the % gain when you would be buying on Poloniex and selling on Binance. Red line represents the value of loss in the opposite direction – the % you would loose in case you would buy on Binance and sell on Poloniex. If the value of gain is negative, the value of loss is positive – that is why red line is above 0. When designing MultiTrader charts I chose to draw loss for the opposite direction rather than gain, as this is much more useful for the Red Phoenix arbitrage described in another article. Anyway, as you can see, the gain on our arbitrage is the highest at 10:10 am, it reaches 5%! This value already covers the trading commissions, however it doesn’t cover the withdrawal fees.
Detailed analysis
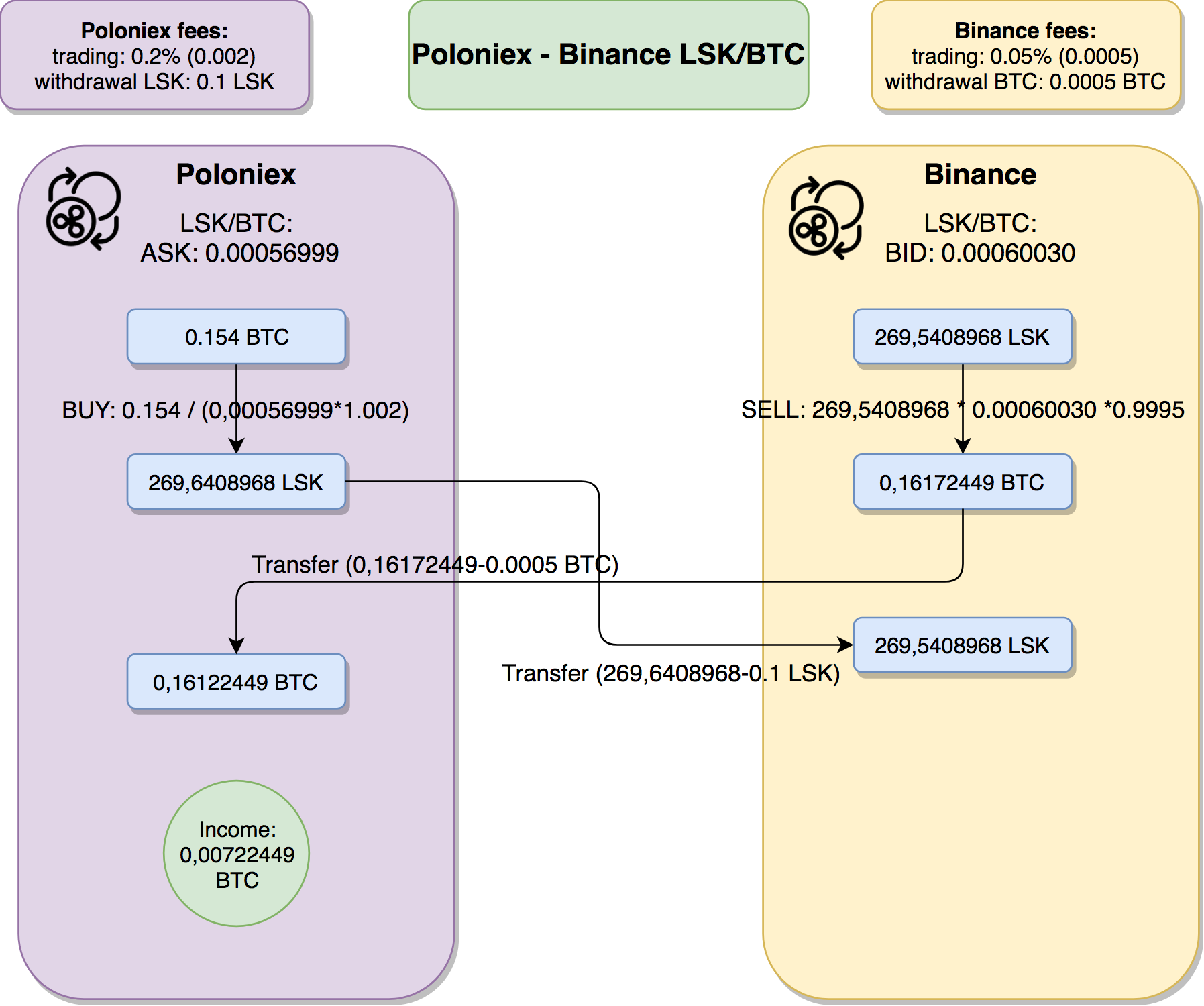
As you’ve seen on the arbitrage analysis screen, I’ve assumed that the size of single transaction will be 1000 USD – that is around 0.154 BTC.
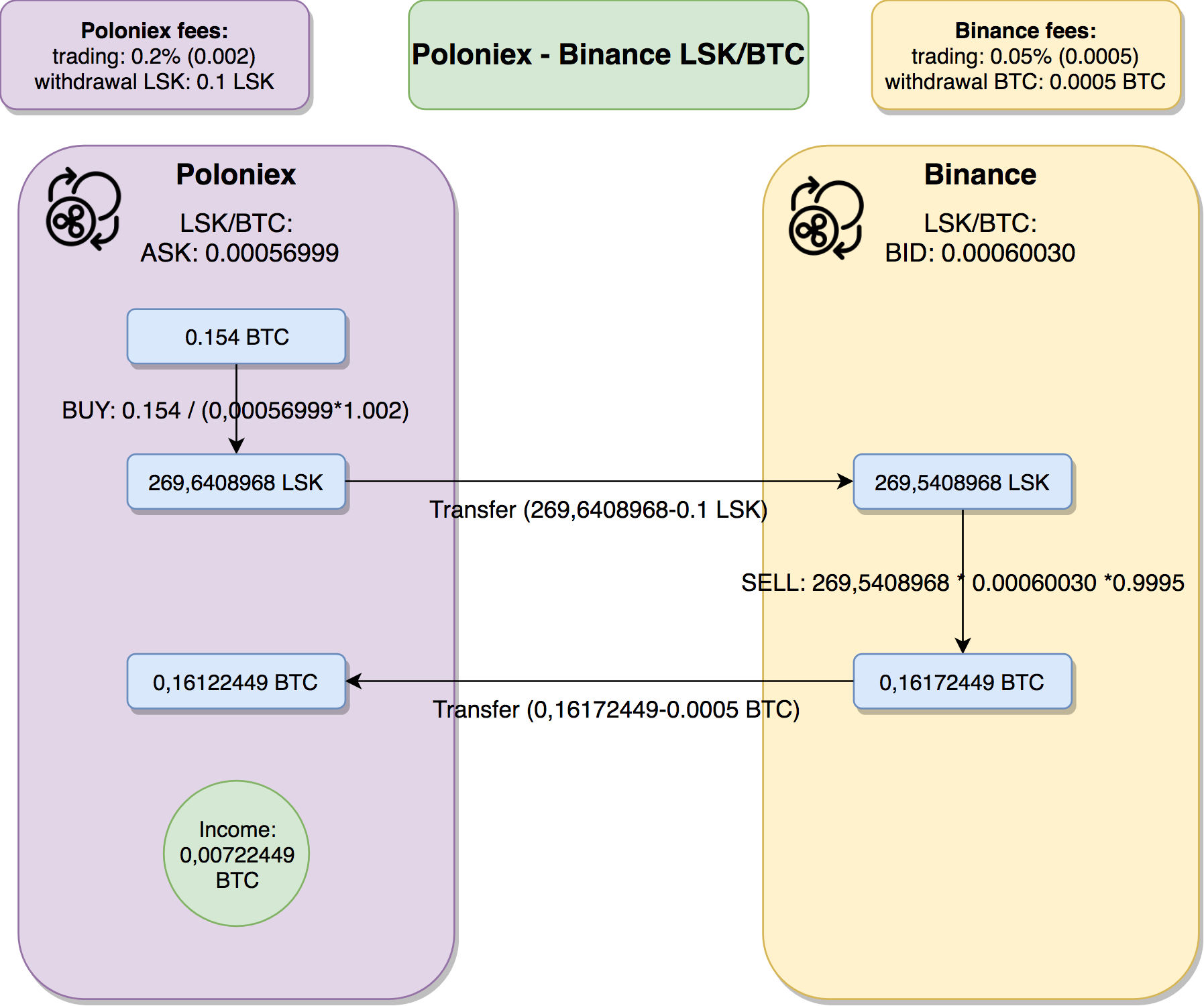
In order to do our math we need to take under account commissions – when we buy on Poloniex we need to pay 0.2% trading fee (it is going to increase the amount we need to pay – therefore we need to multiply the price ASK price by 1.002), when we would like to sell on Binance, we will pay 0.05% trading fee (it is going to decrease the amount we are getting – therefore we need to multiply the price when selling by 0.9995). Let’s go through this flow in steps:
- We are starting with 0.154 BTC on Poloniex
- We are spending our whole 0.154 BTC on Poloniex, buying as much LSK as we can. We get 269,6408968 LSK
- Now, we are withdrawing our LSK from Poloniex to Binance. The withdrawal fee is constant on majority of the exchanges and doesn’t depend on the amount that we are withdrawing. In this case it is 0.1 LSK. The amount of the withdrawal fee is driven by the exchange from which we are withdrawing. That is pretty significant factor that we need to take under account with this kind of arbitrage – the amount of money we need to invest in order to profit is depends on the withdrawal fee. We will come back to this in a second.
- Some exchanges also mention deposit fee, however I think this is some song of the past, as nowadays it is always 0%.
- After transferring our LSK from Poloniex to Binance, we have269,5408968 LSK
- We are selling all of it for BTC. As we are selling we need to look for the BID price – that is 0.00060030 LSK/BTC.
- We also need to pay 0.05% trading fee when selling – we will get 0.05% less when selling – it means we will get 0,16172449 BTC
- Now to do a full cycle, we need to send BTC from Binance back to Poloniex. We need to pay Binance withdrawal fee for BTC – that is 0.0005 BTC.
- After transferring our BTC to Poloniex we have 0,16122449 BTC, that is 0,00722449 BTC more than we had before! That is 4,6% gain. If we express these amounts in USD, we’ve started with 1000, now we have 1046!
The most important concern here is that the transfer takes time. In case of BTC, it may take 20 minutes or more until we see our funds back on Poloniex. In case of LSK it is much faster but still, some exchanges take their time until they schedule actual transfer across wallets on the blockchain just to “process your withdrawal request”. During this time everything may change. First of all the difference between the price on two exchanges may be gone. In our case it may turn out that Binance price will fall the the same level for which we have bought on Poloniex. We will end up not earning anything, but loosing funds on trading and withdrawal fees. It may be even worse. In 30 minutes everything may happen and the price of the asset on which we are doing arbitrage may fall by 20% or more – we have seen such things in the world of crypto, right? This doesn’t necessarily follow the definition of arbitrage – we want to benefit without being exposed to the risk. The time aspect needed for the transfer in fact doesn’t let this method to be effective method for arbitrage. There is a solution to this problem, please take a look at the next section.
Paralel version
What if we do both buy and sell simultaneously on both exchanges? Let’s take a look at this diagram:
Assuming we have funds prepared – BTC on Poloniex and LSK on Binance, we simultaneously buy LSK on Poloniex and sell LSK on Binance. Our overall balance of BTC and LSK is maintained. In fact it is bigger – by the amount that we’ve gained in the arbitrage. There is no transfer time risk here. We do the transfer at the end. In the “reload” phase. It doesn’t really matter how much time it will take. Our arbitrage is already done, and we’ve earned! This is much more stable method – we are not dependent on the time it takes to transfer the funds. The downside is that we need to have funds prepared on both exchanges. How to predict that the arbitrage opportunity will occur on particular two exchanges and given currency pair? That is subject for another article.
Repetitions
Let’s try to think big-scale now about the example that we’ve just analysed. Is 46$ a lot? Well, it is and it isn’t. Earning 46$ in couple of minutes with almost no effort is a lot. On the other hand, that is not enough to buy our lambo. If you look at this chart again:
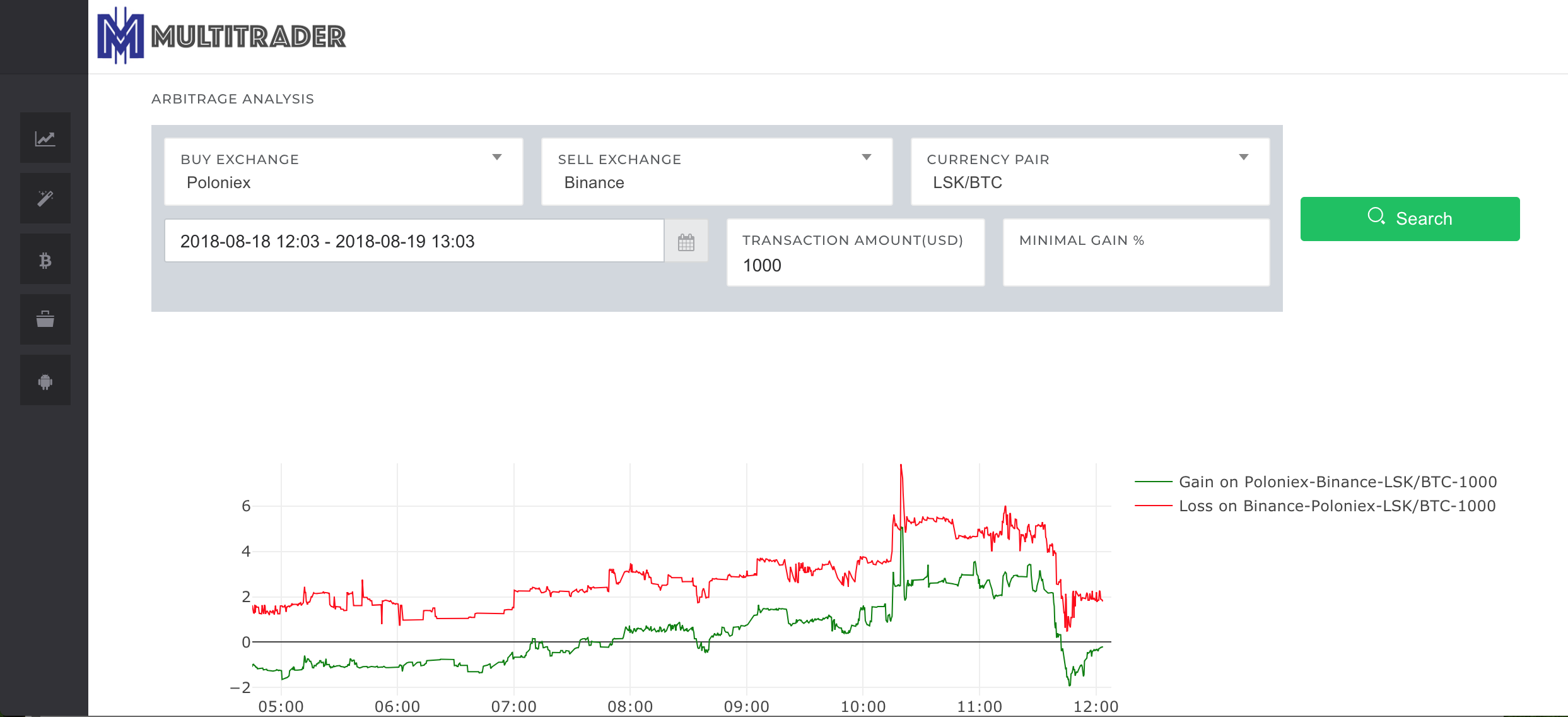
Starting from around 8:40 until around 11:40 we have positive value of gain percentage on the arbitrage (please remember that this value takes under account trading fees but doesn’t cover withdrawal fees – the reason for this is that other arbitrage analysis is general tool that is not targeted towards single arbitrage method and other arbitrage methods do not need withdrawals). Now if we assume that we want to engage only in opportunities that potentially bring us at least 1%, our window starts around 10:20 and ends around 11:40. The time for the single arbitrage operation as described above, will take around 30 minutes. If we start at 10:20, we do the second round at 10:50. It will take again 30 minutes. It ends at 11:20. We’ve already earned a lot and the opportunity seem to continue, we do the third round! After the third round at 11:50 the opportunity is gone…
Is it really going to be like that?
Well, not necessarily. The factor that drives here is the size of the arbitrage opportunity. If your 1000 USD transaction will exhaust the arbitrage opportunity, you will have to be happy with just one round. The size of the arbitrage opportunity is driven by the number of ASK orders on Poloniex available for price lower than BID orders on Binance. That is something that you can actually count! MultiTrader provides you with the tool to do detailed arbitrage analysis. The screenshot below represents this functionality for another arbitrage opportunity that occured on 21st August, three days later after the one that we’ve described in this article:
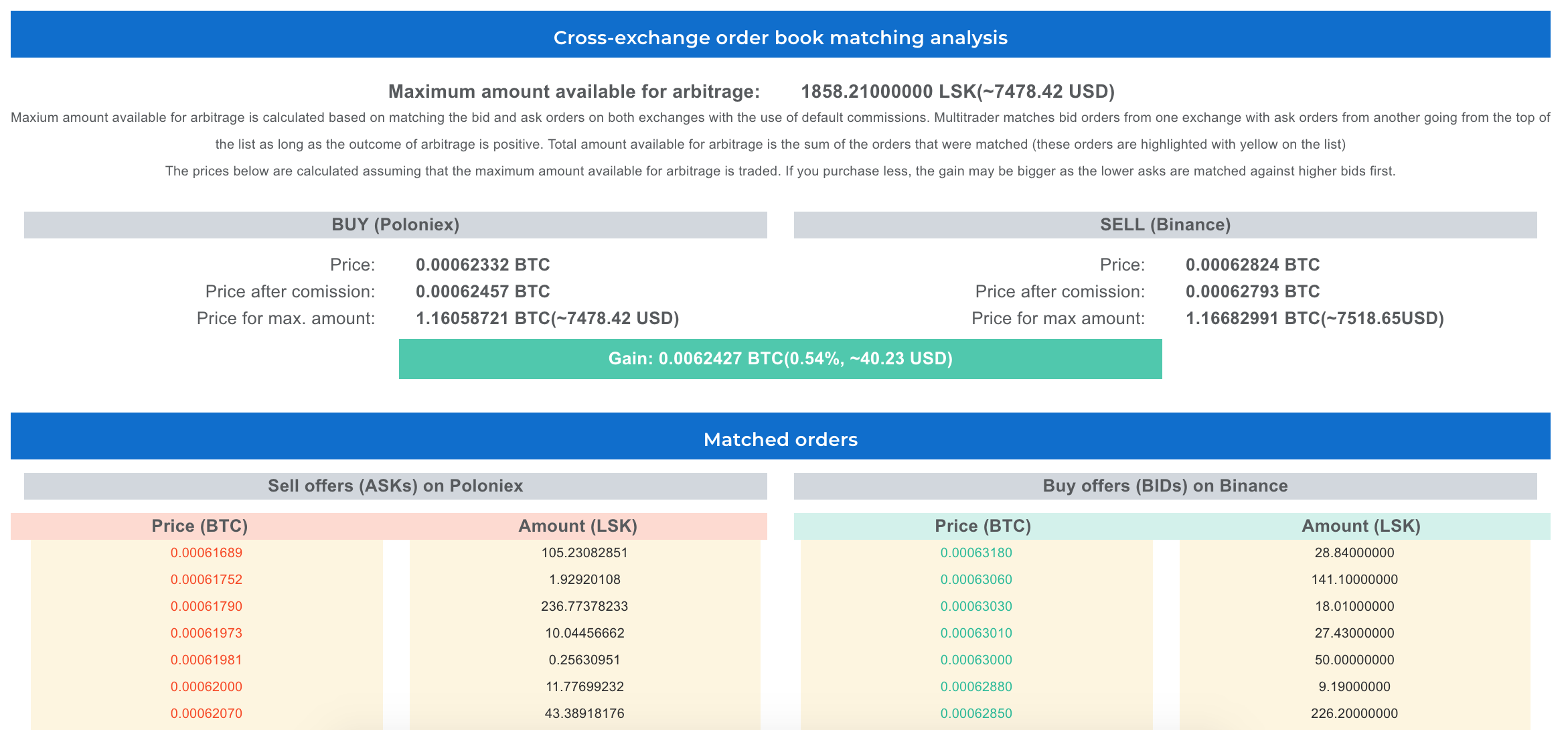
MultiTrader has matched Poloniex ASK orders with Binance BID orders in order to come up with the arbitrage opportunity size. In this case the amount available for arbitrage – that is the arbitrage opportunity size – is 1858 LSK – that is around 7478 USD.